The Ion exchange resin is widely used in various industrial scenarios, and is the basic material used in the chemical industry. In today’s blog post, I will discuss the basics of ion exchange resins, applications of ion exchange resins, and how to regenerate ion exchange resins
What are Ion Exchange Resins?
Thee ion exchange resin is a kind of polymer compound with a functional group, an active group with exchange ion reticular structure and in solubility, usually spherical particles.
The pore structure is divided into gel type and macro pers type. All the resin with physical pore structure is called macro presen, and the macro purse is added as prefix in full name. If the classification is acidic, then cation should be added before the name. The classification should be alkaline, and the word anion should be added before the name; for instance; macro pers strong acid styrene, cationic exchange resin
Ion exchange is a reversible synthetic response where broken up particles are expelled from arrangement and replaced with other ions of the same or similar electrical charge.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Work?
To better understand, how ion exchange resins work, first we need to understand the principles of the ion exchange reaction. To put in simple words, ion exchange can said to be a revocable interchange of charged particles—or ions—with opposite charge particles. This happens when particles present on an insoluble IX gum lattice successfully swap places with particles of a comparable charge that are available in an encompassing solution
The ion resin functions this way for its functional groups, they are essentially fixed ions which are permanently bound within polymer matrix of resin. These charged ions will create bond with ions of an opposing charge, which are conveyed through the use of a counter-ion arrangement. These counter-ions will keep on holding with the practical gatherings until harmony is reached.
During procedure, the treated solution would be added to ion resin bed and let it flow through the beads. As the solution moves through ion resin, the functional groups of resin attract counter-ions present in inside solution
If functional groups have a more noteworthy partiality for the new counter-ions than those effectively present, then the ions in solution will remove the current particles and have their spot, holding with the utilitarian gatherings through shared electrostatic fascination. As a rule, the more prominent the size or potentially valency of a particle, the more noteworthy proclivity it will have with particles of a contrary charge.
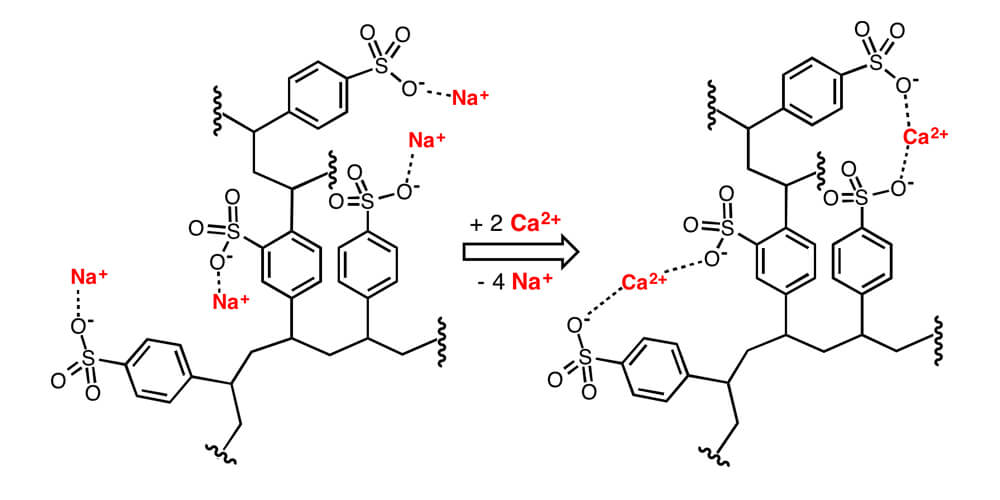
If we apply these concepts to a typical ion water softening system. Then in this case, the softening mechanism comprises of a cation trade tar where sulphonate anion (SO3–) useful gatherings are fixed to the IX pitch framework.
A counter-ion arrangement containing sodium cations (Na+) is then applied to the tar. The Na+ are held to the fixed SO3–anions by electrostatic fascination, bringing about a net impartial charge in the tar. During a functioning IX cycle, a stream containing hardness particles (Ca2+ or Mg2+) is added to the cation trade tar.
Since the SO3–practical gatherings have a more noteworthy liking for the hardness cations than for the Na+ particles, the hardness particles uproot the Na+ particles, which at that point stream out of the IX unit as a feature of the treated stream. The hardness particles (Ca2+ or Mg2+), then again, are held by the IX pitch.
If you need best recommendation for ion exchange resin manufacturer to boost your business, then Rongkepolymer is the most reliable name in China, as well in entire B2B world.