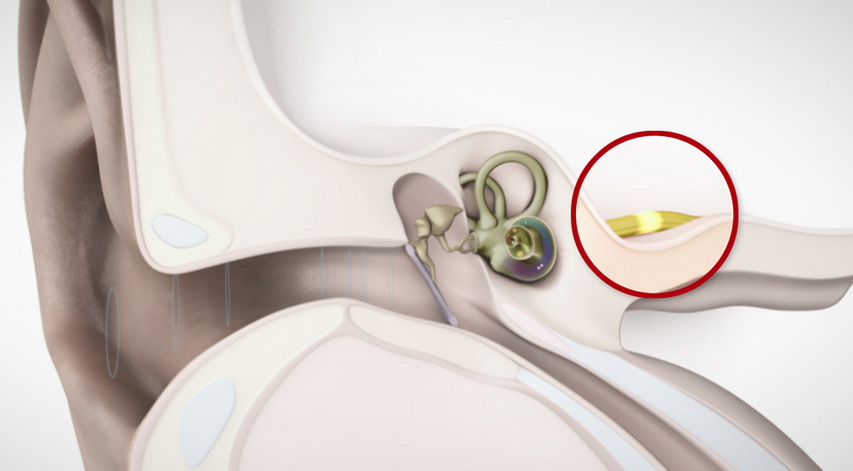
Neural hearing loss is because of issues with the ear trench, eardrum, or center ear and its little bones (malleus, incus, and stapes).
Having Neural Hearing Loss means that there is damage to the small hair cells known as your inner ear (stereocilia) or the neural pathways that pass from your inner ear to the brain. It normally affects both ears. Once you develop Neural Hearing Loss, you have it for the rest of your life. It can be mild, moderate, severe or deep.
Reasons for Neural Hearing Loss
- Mutation of the external ear, ear trench, or center ear structure
- The liquid in the center ear from colds.
- Ear disease (otitis media – contamination of the center ear wherein a gathering of liquid may meddle with the development of the eardrum and ossicles)
- Sensitivities.
- Poor Eustachian tube work.
- Punctured eardrum.
- Considerate tumors.
- Affected earwax.
- Disease in the ear trench.
- Outside item in the ear.
- Otosclerosis (an inherited issue wherein a hard development conforms to a little bone in the center ear, keeping it from vibrating when animated by sound; read more at NIDCD
Medications for neural Hearing Loss
The medical procedure may address conductive hearing misfortune that is because of the inborn nonattendance of ear trench or disappointment of the ear channel to be open during childbirth, intrinsic nonappearance, abnormality, or brokenness of the center ear structures (for example from a head injury), and otosclerosis
Enhancement might be an answer with the utilization of a bone-conduction portable amplifier, or a precisely embedded, osseointegrated gadget (for instance, the Baha or Ponto System), or a traditional listening device, contingent upon the status of the conference nerve.
Antimicrobial or antifungal drugs are utilized to treat constant ear contaminations or interminable center liquid. Tumors, as a rule, require medical procedures.
Neural Hearing Loss
- Neural hearing misfortune (SNHL) is because of issues of the inward ear, otherwise called nerve-related hearing loss.
- Reasons for Neural Hearing Loss.
- Presentation to uproarious clamor (preventable yet not reversible – see increasingly about anticipation).
- Maturing (presbycusis)
- Head injury.
- Infection or ailment.
- Immune system inward ear illness.
- Heredity.
- Deformity of the inward ear.
- Ménière’s ailment.
- Otosclerosis
- Tumors.
Treatment of Neural Hearing Loss
- Abrupt Neural hearing loss (SSHL), ventured to be of viral inception, is an otologic crisis that is therapeutically treated with corticosteroids.
- Corticosteroids may likewise be utilized to lessen cochlea hair cell growing and irritation after introduction to uproarious clamor.
- Neural hearing loss can happen from a head injury or unexpected changes in gaseous tension (e.g., plane plummet), which can cause inward ear liquid compartment break or spillage, which can be poisonous to the internal ear. There has been variable accomplishment with crisis medical procedures when this occurs.
- Reciprocal dynamic hearing loss for more than a while, likewise analyzed as immune system internal ear malady, is overseen restoratively with long haul corticosteroids and now and then with medicating treatment. Immune system inward ear infection is the point at which the body’s resistant framework misleads its barriers against the internal ear structures to cause harm in this piece of the body.
- Fluctuating Neural hearing loss might be from obscure reason or connected with Ménière’s sickness. Side effects of Meniere’s malady are hearing misfortune, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and vertigo. Ménière’s ailment might be dealt with restoratively with a low-sodium diet, diuretics, and corticosteroids. On the off chance that the vertigo isn’t therapeutically controlled, at that point different surgeries are utilized to dispense with vertigo.
- Neural hearing loss from sickness in the focal sensory system may react to therapeutic administration for the particular illness influencing the sensory system. For instance, hearing misfortune auxiliary to various sclerosis might be switched with treatment for different sclerosis.
- Irreversible Neural hearing loss, the most widely recognized type of hearing misfortune, might be made do with listening devices. When listening devices are insufficient, this sort of hearing misfortune can be precisely treated with cochlear inserts.
Congenital Neural Hearing Loss
Congenital Neural Hearing Loss occurs during pregnancy. It is far rarer. Some causes include prematurity, maternal diabetes, lack of oxygen during birth, genetics, and infectious diseases from mother to child in the womb, such as rubella.
Thanks to newborn screening, some children born with hearing loss are diagnosed immediately and treated with hearing aids or kernel implants to help with language development.
What about a sudden sensual hearing loss?
Most of the time acquired Neural Hearing Loss occurs slowly. However, in rare cases, people may develop sudden sensual hearing loss, causing sudden deafness in one ear. If this happens to you, it is important to get medical care immediately.
How does this affect how you listen?
Neural hearing loss affects the loudness and clarity of sounds you hear. You can also experience a reduced range of sounds that you find comfortable. Meaning, the soft and normal voice is very soft, but the loud voice becomes very quick and can really bother you. (In audiological terms, this is known as “recruitment”).
Neural hearing loss can affect all categories of hearing. However, for people with age-related hearing loss, however, it is typical to experience what is known as high-frequency hearing loss, which results in reduced high-pitched hearing ability.
Many people with Neural Hearing Loss report that they can hear but struggle to understand speech. This is especially true in the presence of background noise and can be frustrating and exhausting to deal with.