You may have heard about Cisco VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) and STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) technologies in your CCNA exams. Cisco VLAN and STP lessons can be seen in CCNA Routing and Switching sections.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
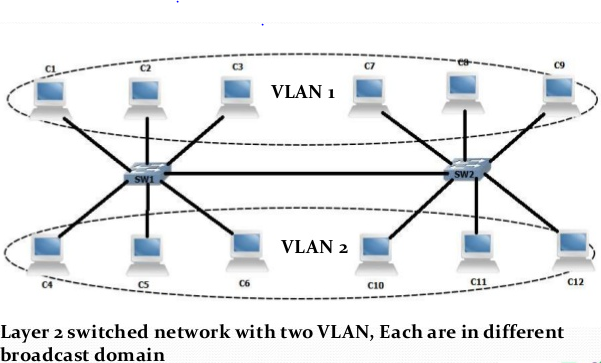
Consider the layer 2 network, here each network segment has its collision domain and also these segments are all having the same broadcast domain. Every device on the network can see every broadcast. Layer 3 devices are mainly used to divide (segment) the broadcast domain into multiple broadcast domains.
In a network, all ports of a switch are in the same broadcast domain. While considering a layer 2 switched networks, a VLAN can be used to divide single broadcast domain to multiple broadcast domains.
In a switched network, the VLANs are not restricted by any physical boundaries, if the switches are used to interconnect the device. A VLAN can be limited within a switch or it can span across the multiple switches. If VLAN is configured as a Layer 3 IP subnet, then you have to use a Layer 3 device (a Router) to have communication between the VLANs.
The main advantages of VLAN are as follows.
Broadcast control: For the normal functions of a network broadcasts are needed. For the proper functioning of the broadcast communication, many protocols and applications are required. If we split the large LAN into small VLANs then each broadcast will only be sent to the exact VLAN, so that we can reduce the broadcast traffic.
Security: VLANs provide better network security. Consider a VLAN network with multiple broadcast domains; here each port and the user are controlled by the network administrator. Using the packet sniffer no malicious user can plug their work station into any port of the switches and sniff the traffic of the network.
Cost: Normally routers are more costlier than switches. So dividing a large VLAN into smaller VLANs is comparatively cheaper than creating a routed network by using the routers.
Physical Layer Transparency: On a physical topology the VLANs are transparent and it is medium transparent over which the network is connected.
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
Broadcast storm is a Layer 2 switching loop that causes serious issues in the communication network. Eliminating this it is one of the main functions of a network switch.
Broadcast storms and Layer 2 switching loop are prevented by using STP in a LAN. In a network the STP allows the redundant links to protect the complete network failure.